How to Use Goal Seek in Excel? (3 Simple Examples)
Note: This tutorial on how to use goal seek in Excel is suitable for Excel 2010, Excel 2013, Excel 2016, and Office 365 users
The Excel Goal Seek feature is one of the easiest ways to solve a single variable problem you are facing. Hurray! You need not use the Excel Solver feature each time, you have a simple equation to solve.
But, there are many pitfalls to look out for while using the Excel Goal Seek function. I’ll cover all these in this guide.
Related:
The Excel Solver Add-in: The Best Explanation In Just 5 Minutes
Excel Sumifs & Sumif Functions – The No.1 Complete Guide
How To Protect Cells In Excel Workbooks-the Easiest Way
Introduction to the Goal Seek Excel function
The Goal Seek function uses a simple user-defined formula and keeps varying any one of its single parameters until it arrives at the user-defined desired output.
Confused?
It is nothing but the good old trial and error method of solving a simple equation, except, Excel does it at super-fast speeds.
Still didn’t get it?
Don’t worry, it’ll be as clear as day after you look at these examples of using the Goal Seek Excel Feature.
Before you want to use the Excel Goal Seek function, keep in mind that you must already know your Goal/Objective value.
That is, Goal Seek in Excel doesn’t solve for the ideal solution, rather it solves for your given value. In fact, it retraces the steps back from your Objective value to find the matching parameter value.
I’ll illustrate goal-seeking easily with these examples.
How to Use Goal Seek in Excel? — Example 1
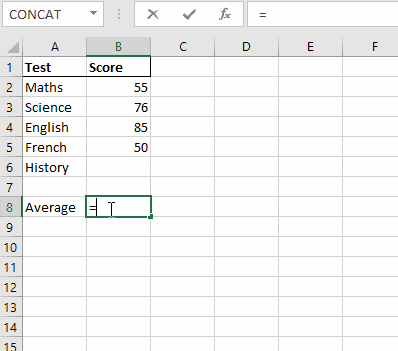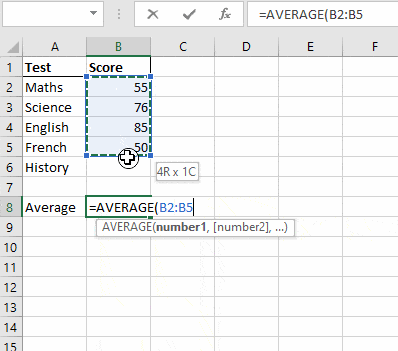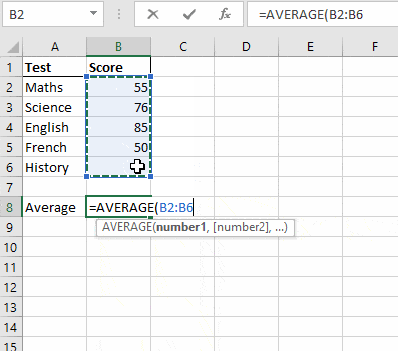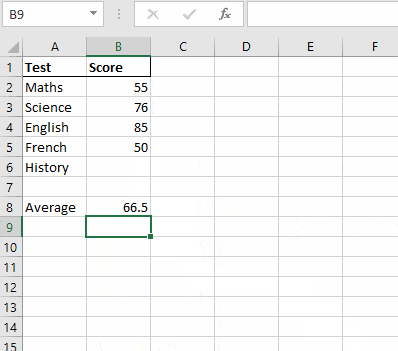
Step 1. Define all the parameters that go into your problem.
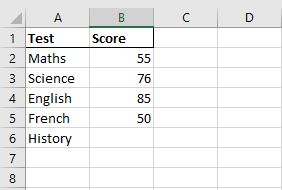
For example, in this case, I have taken 4 out of 5 tests for my final exams and have my scores ready. I need to find out what is the minimum score that I should hit in the 5th test to get an average score of 65 to pass the final exams.
Step 2. List all these parameters, in subsequent rows under the same column

Step 3. In a separate cell express your goal/objective as a formula in terms of the above-mentioned parameters.

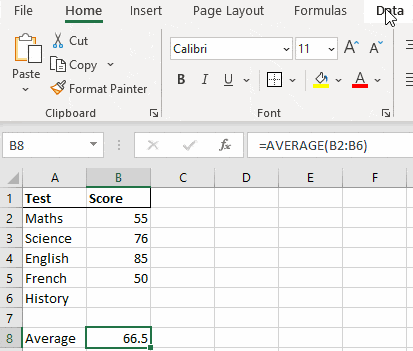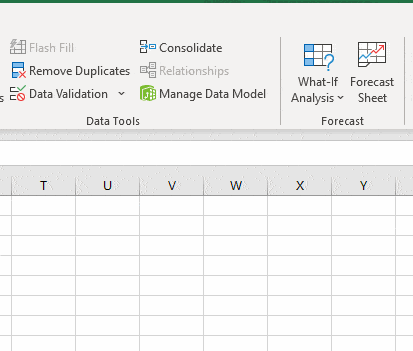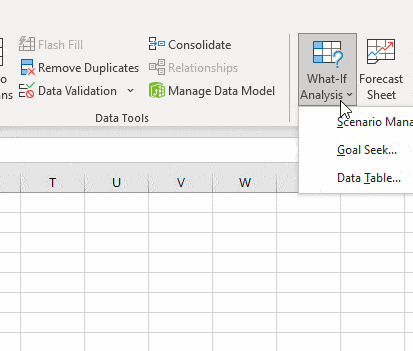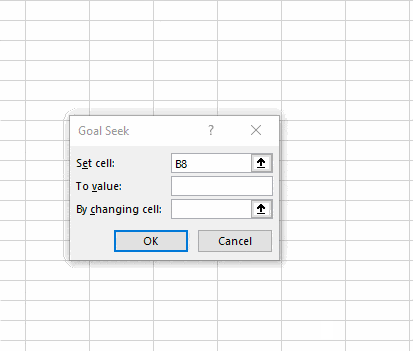
Step 4. Select the cell that contains the goal/objective. locate What-if analysis under the Data Ribbon, and select the Goal Seek button.

Step 5. In the Goal Seek window, select the objective cell under the “Set Cell” option


Step 6. Enter your desired value for your objective/goal by entering it into the “To Value” section.


Step 7. Select the parameter/ assumption that you want to change, under the “By Changing Cell” section.
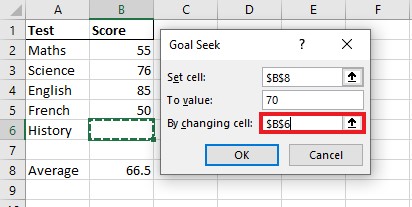

Step 8. Click OK and verify results.


Also Read:
Create An Excel Dashboard In 5 Minutes – The Best Guide
Dynamic Dropdown Lists In Excel – Top Data Validation Guide
Create A Pivot Table In Excel—the Easiest Guide
How to Use Goal Seek in Excel? — Example 2
Here I am going to find the number of units that must be sold, to achieve a target profit of $500. As usual, follow the steps to solve using the Goal Seek Excel function.
Step 1. List all problem parameters and express your goal in terms of these parameters.


Here, my objective cell is total profit. It is defined as profit per unit multiplied by the number of units sold.
Step 2. Set your objective cell, objective value, and the changing parameter under the goal seek window


Here, my goal is to hit a target profit of $500 by varying the number of units sold.
Step 3. Click OK and verify results.


How to Use Goal Seek in Excel? — Example 3
In this example, I want Excel to find the principal amount which yields $500 of interest.
Step 1. List all problem parameters and express your objective in terms of these parameters.
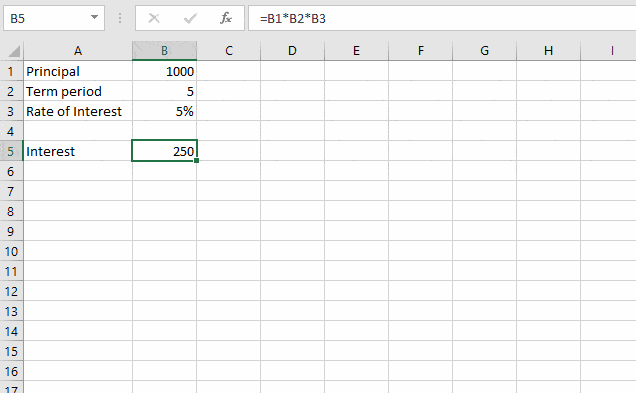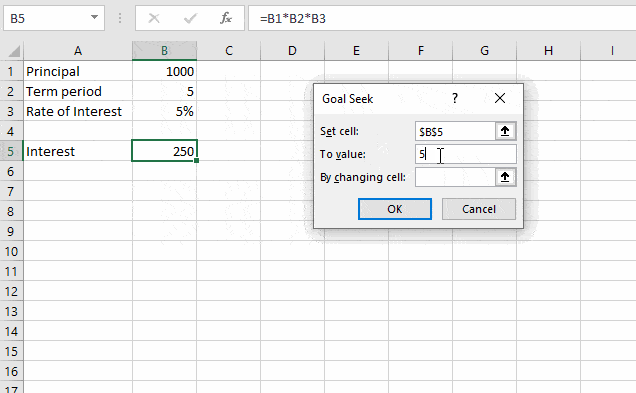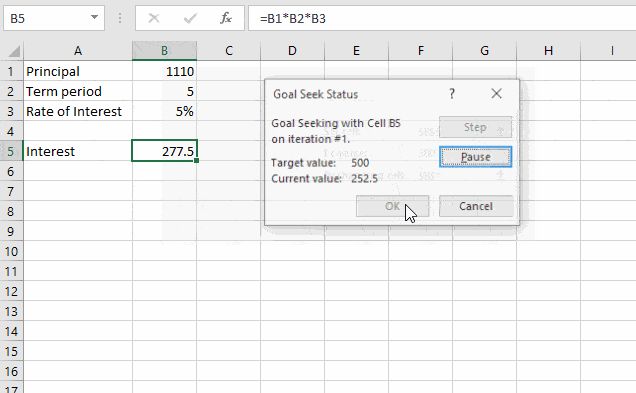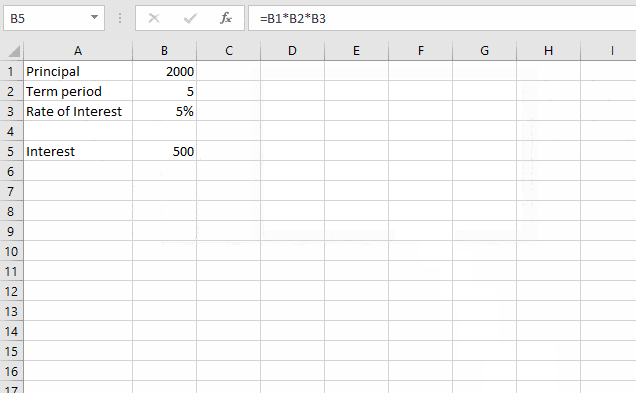
Step 2. Set your objective cell, objective value, and the changing parameter under the goal seek window


Here, the objective is to hit a target interest of $500 by varying the Principal amount.
Step 3. Click OK and verify results.

Suggested Reads:
Excel Conditional Formatting -the Best Guide (Bonus Video)
The Best Excel Project Management Template In 2021
How To Use Excel Countifs: The Best Guide
Limitations of Excel Goal Seek
The Excel Goal Seek feature should not be your only option for solving problems.
It has a very limited problem-solving capacity as it works only with a single input criterion and a single objective formula. Anything more than that needs to be solved with the Excel Solver.
Moreover, it solves for the parameter by plugging in values sequentially. Hence, there might be cases where changing the initial sample parameter value can give you the correct result.
A suitable example is a discontinuous function or an undefined function data point. In such cases, it is wise to enter a starting value that is greater than the said data point for accurate results.
FAQs
What is Goal Seeking?
Goal seeking is the process of guessing the correct input parameter value when the value of the result parameter is already known.
What is the difference between Excel Goal Seek and Solver in Excel?
The Goal Seek feature in Excel solves for a single input cell to achieve the desired objective, whereas the Excel Solver can solve for various input cells to achieve the desired. Moreover, the Solver can account for any problem constraints, whereas Goal Seek Excel cannot handle any constraints.
Let’s Wrap Up
In this Goal Seek Excel tutorial, we have talked about how to use the Goal Seek feature properly with three easy illustrations. But, it is important to remember that it has its own drawbacks.
Goal Seek is a very useful Excel feature to quickly guess required values. It will definitely come in handy during some situations. But keep in mind that it is not a very reliable tool to solve complex problems. Always cross-check your results when it comes to Excel Goal Seek.
If you want to see more high-quality Excel guides like this, visit our free Excel resources section.
If you want to explore our in-depth Excel courses click here.

